Artificial intelligence (AI) has become an important part of modern technology because it has changed many fields, from healthcare to business. It's too bad that AI didn't grow overnight; it took decades of tests and hard work to get to where it is now. The deep learning methods used today are very different from Alan Turing's Illusions. This post talks about the interesting past of AI, focussing on major events and findings that have transformed the field.
The Birth of AI: Turing and Early Foundations
Alan Turing, a British scientist, came up with the idea of machines that could think for itself. A lot of people call him the "father of theoretical computer science." In the 1930s, Turing came up with the idea of the universal machine. It was just an idea that could be used to explain any mathematics process. This idea led to later ones about making tools that could do things that people usually need to understand.
"Computing Machinery and Intelligence," Turing's 1950 work, was the first to propose the Turing Test, a way to see if a machine could behave intelligently in a way that was either the same as or impossible to tell apart from human behavior. Even though it was just an idea at the time, it made people think about how clever tools might be possible.
The Dawn of Artificial Intelligence: 1950s to 1970s

In the years following Turing’s work, AI began to take its first steps toward becoming a reality. The field of AI research was formally established in the 1950s, with key figures such as John McCarthy, Marvin Minsky, and Allen Newell leading the charge. In 1956, the term "artificial intelligence" was coined at the Dartmouth Conference, which is often considered the birth of AI as a field of study.
During the 1960s and 1970s, early AI systems focused on solving specific problems using symbolic reasoning and logical processes. Programs such as ELIZA, a simple natural language processing program created by Joseph Weizenbaum in 1966, showed early promise in mimicking human conversation. These early AI systems were rule-based, relying on programmed instructions to make decisions.
The AI Winter: Setbacks in the 1980s and 1990s
Despite the initial excitement surrounding AI, the field faced significant setbacks during the 1970s and 1980s. The AI Winter refers to the periods of stagnation and reduced funding for AI research caused by disappointing progress. AI systems failed to live up to the high expectations set in the early years, especially when faced with the complexity and unpredictability of real-world tasks.
AI researchers at the time had promised machines that could think like humans, but the limitations of the early AI models became clear. The symbolic AI approach, based on rigid rules and logic, struggled to handle ambiguity and complexity, and this led to frustration within the research community. As a result, many AI projects were discontinued, and funding from governments and private institutions decreased dramatically.
However, during this period, some developments were made in expert systems, which were designed to emulate the decision-making abilities of human experts in specific fields. These systems helped in areas like medical diagnosis and financial planning, but they were far from achieving general AI.
The Rise of Machine Learning: 1990s to 2010s
The 1990s ushered in a new era for AI, driven by the rise of machine learning. Unlike traditional AI, which relies on explicit programming and rules, machine learning focuses on teaching computers to learn from data and improve their performance without being explicitly programmed. This shift allowed AI systems to move beyond fixed rules and adapt to new, unseen data.
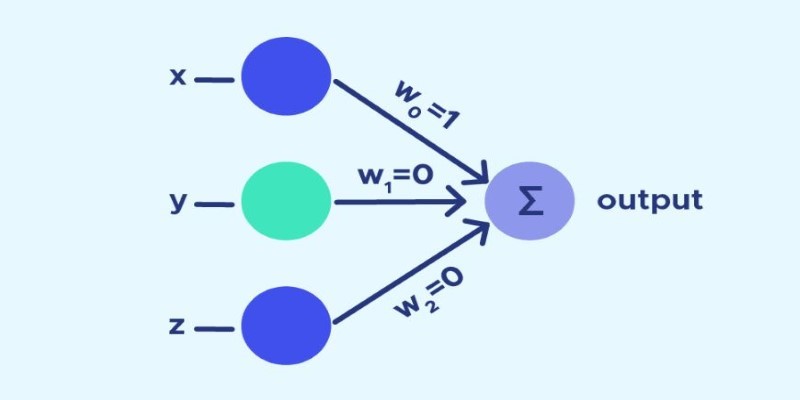
One of the most notable advancements in this period was the development of neural networks—computational systems modeled after the human brain. Neural networks were capable of identifying patterns in data, and researchers developed techniques like backpropagation, an algorithm that helped neural networks train more effectively. While neural networks were still in their early stages, these advances allowed AI to perform more sophisticated tasks.
Deep Learning and Modern AI: 2010s to Present

The 2010s marked the true rise of deep learning, a branch of machine learning that uses big neural networks with lots of layers, which is how the word "deep" came to be used. These deep neural networks could process and learn from vast amounts of data, leading to significant breakthroughs in AI capabilities.
The availability of big data and powerful computing resources, especially through the use of graphics processing units (GPUs), was critical in enabling deep learning. GPUs, originally designed for graphics rendering in video games, were found to be extremely effective at handling the parallel processing tasks required for training deep learning models.
One of the breakthrough moments in deep learning came in 2012 when a deep learning model developed by researchers at the University of Toronto won the ImageNet competition, a major benchmark in computer vision. The model drastically outperformed traditional computer vision techniques, demonstrating the potential of deep learning for complex tasks like image recognition.
Since then, deep learning has become the backbone of many AI applications. It powers systems like self-driving cars, virtual assistants like Siri and Alexa, and image recognition software used in healthcare and social media. The increased accuracy and efficiency of deep learning models have led to their widespread adoption across various industries, making AI a ubiquitous technology.
Conclusion
The history of artificial intelligence is a remarkable journey of innovation, setbacks, and breakthroughs. From Alan Turing’s early theoretical work to the rise of deep learning in the 21st century, AI has evolved significantly. While there are still challenges ahead, the potential for AI to improve our lives is immense. As the field continues to advance, it will be essential to address the ethical concerns surrounding its use to ensure that AI benefits society as a whole.